disease definition
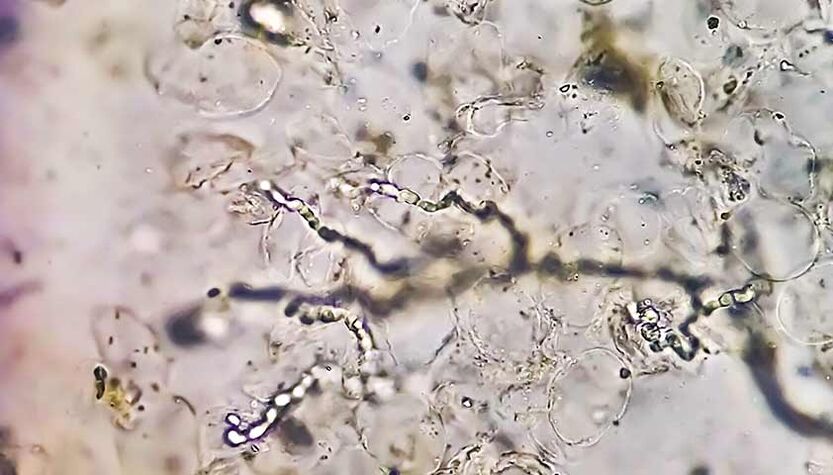
Prevalence of foot mycosis
Causes of foot fungus
- Violation of personal hygiene;
- Sharing shoes (e. g. , at bowling alleys, skate and ski rental shops);
- Visit public baths, swimming pools, beaches;
- Climate characteristics: Countries with subtropical and tropical climates have a higher risk of illness – this is due to increased humidity and ambient temperature;
- Frequent wearing of closed, tight-fitting shoes (this occurs in military personnel, miners, and workers in the textile and metallurgical industries);
- Toes are often injured due to flat feet, calluses, and corns;
- Failure to observe hygiene rules during pedicure;
- Impaired blood supply to the legs;
- immunodeficiency diseases, including HIV;
- chronic skin diseases;
- obesity;
- diabetes;
- chronic venous insufficiency;
- Taking certain medications (systemic corticosteroids).
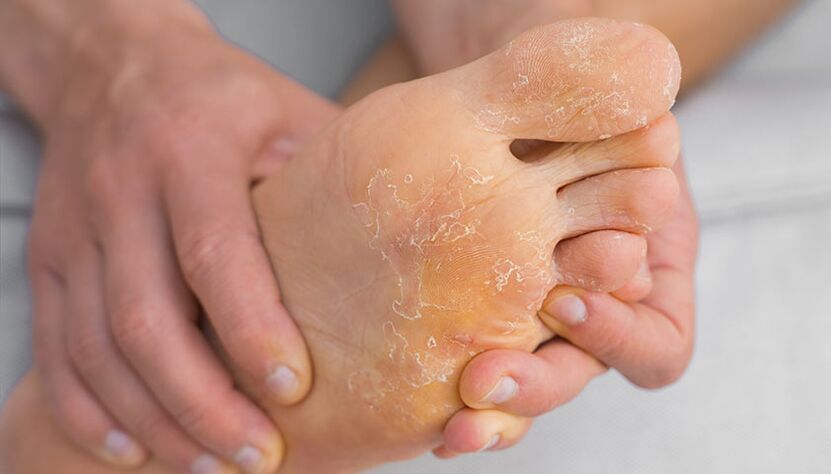
Symptoms of foot fungus
Squamous (squamous hyperkeratosis) form of fungal disease of the feet
Interdigital (interdigital) form of fungal disease
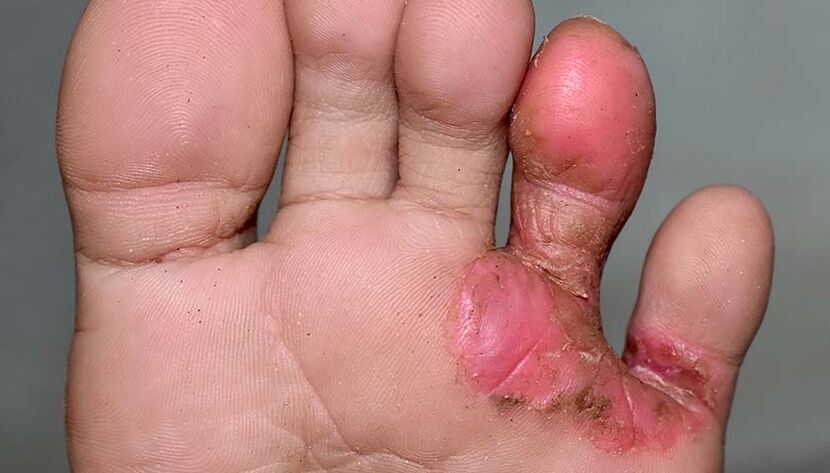
Dyshidrotic forms of foot mycosis
Exudative diaphoretic foot mycosis
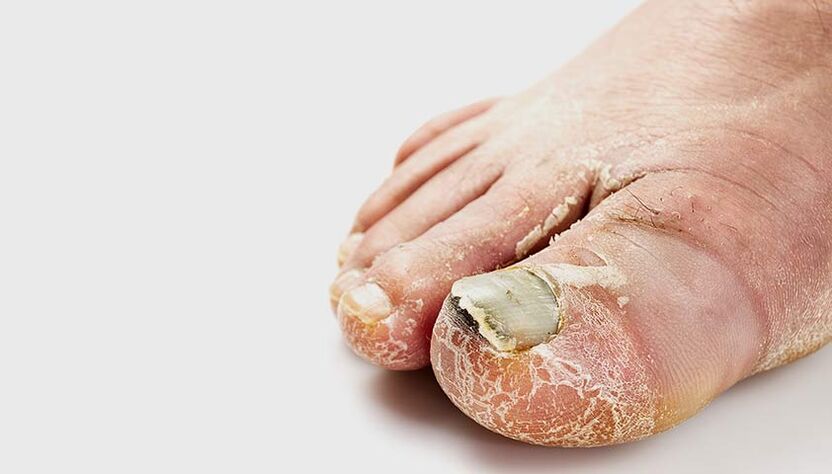
Elimination forms of foot fungus
Acute forms of foot mycosis
Vesicular bullous (inflammatory) mycosis of the feet
Ulcerative forms of foot mycosis
Complications of foot fungus
- Infectious and drug-induced allergic dermatitis;
- Pyoderma - pustular skin disease (cellulitis, lymphangitis, cellulitis, osteomyelitis of the feet) that can cause deep, long-lasting skin wounds;
- plantar warts;
- Microbial eczema is a chronic inflammatory disease that causes itchy, red skin with fluid-like blisters;
- General decline in immunity and impairment of microcirculation in the lower limbs (commonly seen in patients with diabetes and varicose veins);
- Spread of disease to the skin and nail plates of the hands;
- Deterioration of quality of life: Acute fungal disease makes it difficult to wear shoes, lymphadenitis can lead to fever and poor health.

Diagnosis of foot fungus
Treatment of foot fungus
Treatment options and drug dosages are determined by your doctor. During treatment, it is necessary to visit a podiatrist at least once a month.
prognosis and prevention
- Change socks every day, or more often if your feet are sweaty or damp;
- Allow shoes to dry after wearing;
- Use an antifungal UV shoe dryer;
- Please do not wear shared slippers when visiting;
- Don’t try on shoes in a store barefoot;
- Use a personal towel to wipe your feet;
- Use separate nail care tools (tweezers, files);
- Wear shoes in the pool or sauna;
- Monitor dietary diversity;
- Avoid stressful situations.